Table of Contents
ToggleWhether you find yourself in the role of a caregiver, a healthcare professional, or supporting a family member through the process of moving from bed to wheelchair, there’s no need for apprehension.
The task of transferring patients need not be daunting. Instead, it’s an opportunity to understand the techniques involved and create a secure and comfortable experience for the individual.
This guide aims to delve into the intricacies of achieving smooth transitions while upholding the dignity and peace of mind of the person being transferred.

Grasping the Fundamentals
Before embarking on the practical procedures, it’s paramount to lay down some fundamental principles. Safety takes precedence above all. Begin by assessing the patient’s condition thoroughly and seek guidance from healthcare experts if needed.
Ensure that both the bed and wheelchair are appropriately adjusted in height, not only to reduce strain on your back but also to facilitate a seamless transfer for the patient.
Creating a secure and comfortable experience during the transfer process requires attention to detail and adherence to safety protocols.
Reading Suggestion: emirates wheelchair assistance
Key Importance of Preparation
1. Evaluate the Patient’s State
Prior to commencing any transfer, assess the patient’s overall health. Gain insight into their physical abilities, existing injuries, areas of discomfort, or any limitations they might have.
2. Ensure Path Clearance
Guarantee a clear passage from the bed to the wheelchair by removing obstacles. Secure the wheelchair’s wheels to maintain stability during the transfer.
3. Employ Suitable Tools
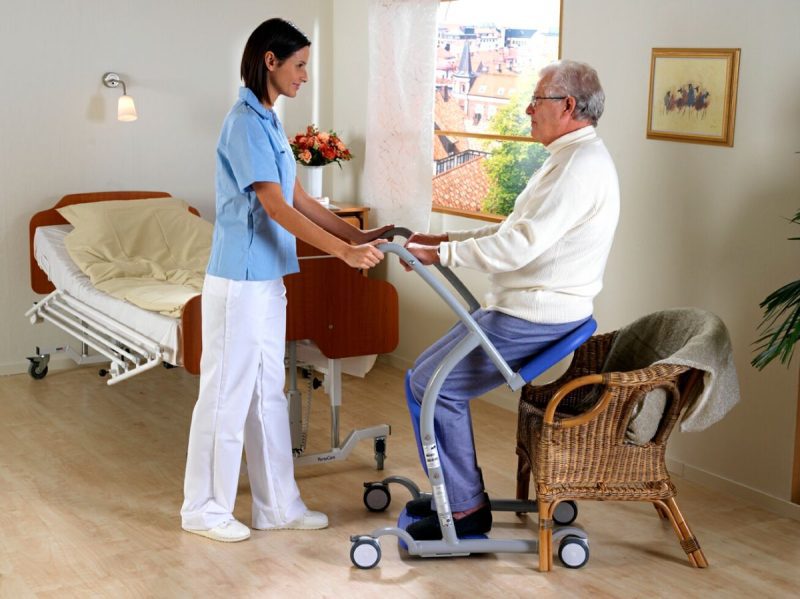
Utilize supportive aids like transfer belts, slide sheets, or hoists as per the patient’s requirements and the caregiver’s abilities.
Explore: Electric wheelchair price in UAE
Sequential Instructions
Vital Communication
Engage with the patient, detail each phase, and request their cooperation. Confirm their comfort and readiness for the transfer.
Arranging the Wheelchair
Position the wheelchair near the bed, ensuring it’s slightly angled to facilitate smoother handling. Secure the wheels to prevent any unforeseen motion.
Correct Body Mechanics
Keep your back straight, bend your knees, and employ leg muscles instead of your back while lifting. Steer clear of twisting your body; opt for pivoting your feet for movement.
Utilizing a Transfer Belt
When accessible, employing a transfer belt encircling the patient’s waist offers added support, enhancing safety for both parties involved. Ensure a secure fit without excessive tightness.
Aiding the Patient
Guide the patient into a seated position with their feet planted firmly on the floor. If they possess adequate strength, motivate them to independently rise. If assistance is required, gently aid them, providing necessary support as they bear their weight.
Preparing for the Transfer
Stand in front of the patient, positioned slightly to the side. Maintain a stance with your feet apart at shoulder width to ensure enhanced stability.
Lifting Technique
Position one hand beneath the patient’s distant hip and the other beneath the upper back or shoulder region. Lift the patient using the strength of your leg muscles, not relying on your back, after counting together.
Directing the Motion
Coordinate your movements, guiding the patient towards the wheelchair. Lower them into the seat gently, ensuring their comfort and proper positioning.
Fine-Tuning
Implement any required modifications to guarantee the patient’s comfort and safety. Unlock the wheelchair wheels and verify their stability before initiating movement.
Assistance and Ease
Extend support while the patient adjusts to the wheelchair, supplying pillows or extra cushions if necessary for added comfort.
Pointers for a Seamless Transition
- Skill Comes with Practice
If you’re inexperienced in transferring patients, rehearse with a healthcare professional to gain confidence and ensure the correct method is employed.
- Exercise Patience
Avoid hastiness as it can lead to accidents. It’s preferable to proceed slowly and cautiously rather than hastily, prioritizing safety.
- Tailor to Unique Needs
Recognize the individuality of each patient. Adjust your approach based on their capabilities and comfort levels.
- Seek Assistance When Required
If the patient’s weight is challenging or specialized equipment is necessary, don’t hesitate to seek additional help. Having more hands available ensures a safer transfer.
Explore: Wheelchair Rental Dubai
Post-Transfer Assistance
Once the patient is comfortably seated in the wheelchair, ensure their essential items are within reach. Double-check their comfort, fasten any required restraints securely, and maintain a supportive presence throughout the post-transfer phase. This includes a continuous reassurance of their well-being and readiness to assist further if needed, fostering a sense of security and comfort after the transfer.
Final Thoughts
Conducting patient transfers from bed to wheelchair might seem daunting, but with the application of proper techniques, thorough preparation, and a patient approach, a safe and seamless process is achievable.
Simultaneously, upholding correct body mechanics reduces the risk of injury for both the caregiver and the patient, emphasizing the significance of maintaining a stable posture during the transfer.
Tailored care remains pivotal; recognizing and accommodating specific requirements enriches the overall transfer encounter. Emphasizing safety and comfort remains paramount; they serve as the linchpins for a successful transfer.
Armed with these invaluable insights, caregivers and healthcare practitioners can turn what appears challenging into a smooth and comfortable experience for all involved.
Embracing these methodologies transforms patient transfers from intimidating tasks into well-executed procedures, fostering feelings of safety and comfort for both the patient and the caregiver.